What is Thunderbolt Technology?
Users have long wanted desktop - level performance from a portable computer. Thunderbolt was developed to create new user experiences by simultaneously supporting the fastest data and most video bandwidth available over a single cable, as well as supplying power. Thunderbolt allows users to connect to two monitors that supports mini DisplayPort or DisplayPort connections. Adapters can allow for HDMI, DVI and VGA connections as well.
Thunderbolt 1 and 2 uses the same connector as MiniDisplayPort and Thunderbolt 3 uses USB Type C.
Thunderbolt 3 Connection Modes. Thunderbolt 3 dynamically detects the capabilities of the cables and devices that are plugged in. Several modes can be detected and activated, in a way that is generally transparent.
USB Only Mode. If a USB device is plugged in, a USB Host controller inside the Thunderbolt 3 Enabled system is activated, and the Thunderbolt 3 silicon PHY drives USB (2.0 , 3.0 or 3.1 ) signals to the USB C port. In this mode, the thunderbolt 3 port behaves exactly like a typical USB 3 3.1 enabled connector.
DisplayPort Only Mode. If a DisplayPort Display or adapter is plugged in, the Thunderbolt 3 enabled system will detect this and switch the pins driving the USB C connector to the DisplayPort alternate mode. Thunderbolt 3 silicon will then act as a router to send raw DisplayPort traffic from the graphics engine within the system out over the USB C connector pins, and pass that DisplayPort link directly to the display or adapter.
In this mode, a Thunderbolt 3 enabled USB C port will support a single four -lane (4 x5.4 Gbps , or HBR2 ) link of DisplayPort. These four links run across the two pairs of high speed wires in the USB-C connector and cable. This kind of DisplayPort link can support a single, uncompressed display at 4K resolution at 60 Hz.
DisplayPort and USB Mixed Mode. In this alternate mode of operation, one of the high speed connector pin pairs of signals will be dedicated to DisplayPort (now two lanes at 5.4 Gbps) and one to USB 3.1. This allows for basic connectivity for data and display devices such as docking stations or data and display dongles. With two lanes of DisplayPort 1.2a resolutions at Quad HD (QHD) can be achieved or 2560x1600 at 60Hz.
Thunderbolt 3 Mode. If a cable and device supporting Thunderbolt are plugged in, the Thunderbolt silicon activates its highest capability mode, and links two bidirectional links at either 10Gbps or 20Gbps or 40Gbps. Additionally, to fill this Thunderbolt link, the silicon extracts and routes up to four lanes of PCI Express Gen 3 ( 4 x 8 Gbps ) and up to two ( four lane ) full links of DisplayPort out over the Thunderbolt cable and connector to the device(s) attached downstream from the host system.
Thunderbolt Networking Mode. An additional powerful capability of Thunderbolt allows to or more hosts to be connected directly ( or on separate ends of a Thunderbolt chain ) via Thunderbolt. In this case, Thunderbolt has software that creates an IP networking link between these systems.
This networking mode allows for the Thunderbolt interface to act as a virtual Ethernet adapter and transfer traffic over the PCI Express interface that the Thunderbolt silicon has in each host system.
Power Delivery and Charging. In each of the modes listed hereby, the Thunderbolt 3 system ( if designed to support this by the system manufacturer ) can also request to charge over the connector from a device or adapter designed for delivering power to the system up to 100W via the USB PD Specification.
In this way the Thunderbolt 3 enabled USB C Connector can support charging, display, data or all three at the same time in various configurations.
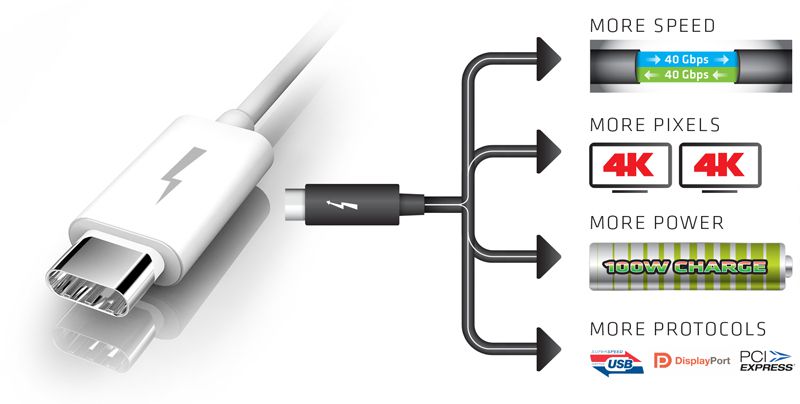
What is Thunderbolt 3
Thunderbolt is a sophisticated technology, with a simple vision : the USB C that does it all. Thunderbolt 3 is the single connector that can deliver on all your connectivity needs. Connect to a dock and expand to your legacy peripherals. Directly cable to a monitor or two. Or connect to a single ( or series ) of high performance, dedicated Thunderbolt device.
Thunderbolt™3 One port does it all
You can do all this and more with a single connector through which you can also charge your system. Thunderbolt 3 builds on the new USB C reversible connector and integrates the latest USB 3.1 technology to deliver high performance and compatibility to the existing standard.
How Does Thunderbolt 3 Work?
Fundamentally, Thunderbolt is a tunneling architecture designed to take a few underlying protocols and combine them onto a single interface. That way, the total speed and performance of the link can be shared between the underlying usages of these protocols – whether they are data, display, or something else.
At the physical interface level, Intel’s Thunderbolt 3 silicon builds in a few important features: A physical interface (PHY) layer that can dynamically switch its operating mode to drive either:
• USB 2.0, 3.0, and 3.1
• DisplayPort* 1.1 and 1.2a
• Thunderbolt at 20 Gbps and 40 Gbps
In the Thunderbolt mode, the Thunderbolt 3 port has the ability to support at least one or two (4-lane) DisplayPort interface(s), and up to four lanes of PCI Express Gen 3.
Video Performance
Thunderbolt Graphic offload all the heavy lifting of HD Video Playback and 3D Rendering to the GPU of your device. If your GPU performance is good you can even play games on a 4K Monitor.
Thunderbolt Graphic provide support for HDCP ( this is a form of Content Protection) which will allow you to enjoy your favourite movies
For Apple users: Apple display settings will hide the resolution, so please hold down the option button on the Apple display resolution interface and then click zoom position of the resolution interface to display the hidden resolution. Then check the real resolution.
Discover True Detail
4K also known as Ultra High Definition (UHD) delivers four times as much details as 1080p Full HD, that is eight million pixels compared to two million pixels, bringing more image clarity, fine detail and greater texture.

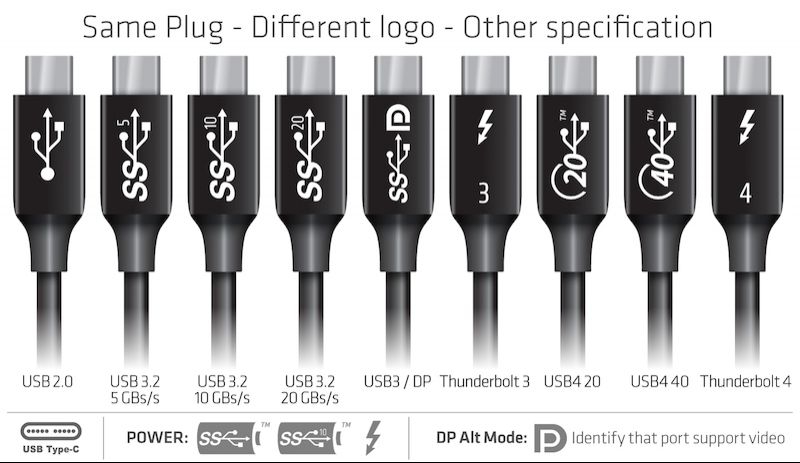
Symbols on USB-C Plugs

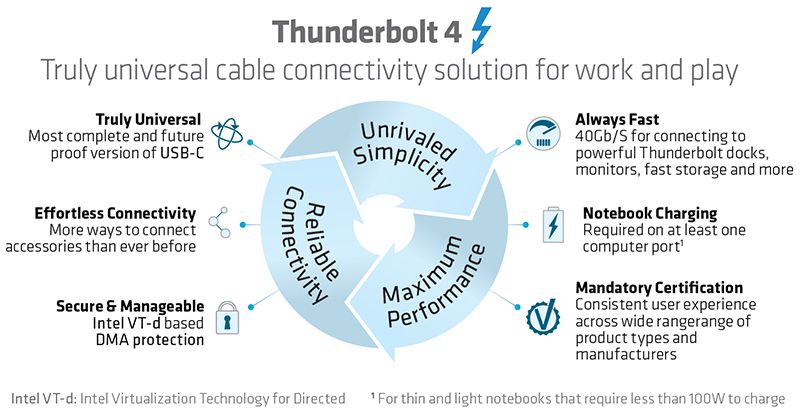
Introducing Thunderbolt 4
Intel revealed new details in July 2020 about Thunderbolt™ 4, the next generation of its universal cable connectivity solution, delivering increased minimum performance requirements, expanded capabilities and USB4 specification compliance.
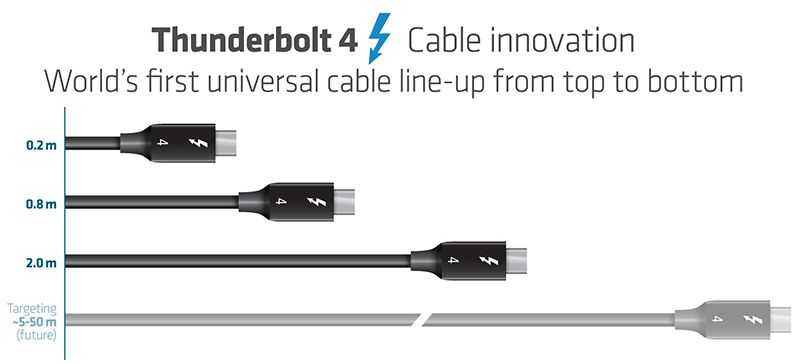
For the first time, Thunderbolt 4 will offer docks with up to four Thunderbolt ports and universal cables up to 2 meters in length. Intel’s upcoming mobile PC processors, code-named “Tiger Lake,” will be the first to integrate Thunderbolt 4.
Thunderbolt provides consumers with a leading connectivity standard across a range of devices, helping to advance computing experiences and delivering on the promise of USB-C with simplicity, performance and reliability. The arrival of Thunderbolt 4 underscores how Intel is advancing the PC ecosystem toward truly universal connectivity solutions.
Why Does It Matter?
Thunderbolt products deliver a consistent, industry-leading set of capabilities for connecting computers to data, video and power with the simplicity of just one USB Type-C port.
Connect to powerful Thunderbolt docks, displays, fast storage or any USB accessory for a clutter-free workspace.
Thunderbolt 4 Connectivity
What Does It Deliver?
Thunderbolt 4 builds on the innovation of Thunderbolt 3 for a truly universal cable connectivity experience. Thunderbolt 4 always delivers 40 Gbps speeds and data, video and power over a single connection. It is the most comprehensive Thunderbolt specification yet with compliance across the broadest set of industry-standard specifications – including USB4, DisplayPort and PCI Express (PCIe) – and is fully compatible with prior generations of Thunderbolt and USB products.
Thunderbolt 4 certification requirements include:
• Double the minimum video and data requirements of Thunderbolt 3.
- Video: Support for two 4K displays or one 8K display.
- Data: PCIe at 32 Gbps for storage speeds up to 3,000 MBps.
• Support for docks with up to four Thunderbolt 4 ports.
• PC charging on at least one computer port .
• Wake your computer from sleep by touching the keyboard or mouse when connected to a Thunderbolt dock.
• Required Intel VT-d-based direct memory access (DMA) protection that helps prevent physical DMA attacks.
Please refer to a full overview of our Legacy Terms and Conditions on www.club-3d.com.

 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Türk
Türk